Produce "fire" dispersion
Dispersion is a phenomenon in which mineral gemstones decompose complex light into monochromatic light. When white light is injected into a honed, gemstone with a certain angular angle, different monochromatic lights will have dispersion due to the difference in refractive index, and the seven colors from red to purple are separated, which is the same as the prism. The colorful, brilliant flashing “fire†produced by the dispersion adds to the beauty of the gem and makes it more attractive.

Polychromaticity
The pleochroism of a gem is a phenomenon in which a crystal exhibits different colors in different directions under transmitted light. The reason for this is that the heterogeneous minerals have different internal structures, which cause changes in light wave absorption in different directions, resulting in different colors, generally dichroism and trichromaticity, and the color of various gemstones is still inexhaustible. The same, this can be used as one of the means of identification.

Special optical effect
The root cause of the special optical effect of gemstones is that in the formation process of gem minerals, the interior contains various special conditions such as inclusions, twin crystals, and spherical particles, which cause interference, diffraction, and scattering of light. This is basically a feature that can be displayed by curved gemstones. These characteristics are manifested in the following effects:
(1) Cat eye effect. Under the illumination, the curved gemstone will show a flashing light band (playing color), which is like a cat's scorpion, so it is called opal because the mineral contains dense and small parallel fiber-like and needle-like inclusions. The light strip is perpendicular to the inclusions). Due to the scattering effect of light, the white light is deviated from the original direction, and then the "cat's eye" appears through the arc surface. The gold emerald cat's eye is a true (standard) opal, others include quartz cat's eye, tourmaline cat's eye, beryl cat's eye, and apatite cat's eye.
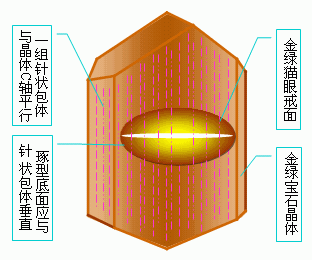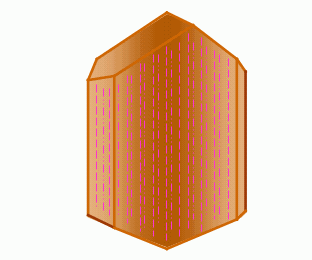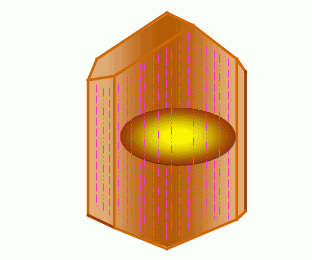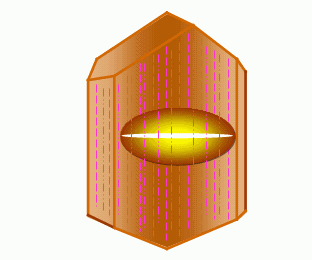

(2) Starlight effect. In other light-emitting gemstones, there are four-, six-, and even twelve-color starlight strips that intersect each other, just like the stars in the night sky. This phenomenon is called the starlight effect. When the vertical fibrous inclusions are cut and polished in the long axis direction, two or three sets of parallel-arranged inclusions intersect at different angles to produce a shiny radial band, which is basically the same as the cat's eye. The starlights are starlight diopside and starlight spinel; the six stars are starlight rubies and sapphires, starlight hibiscus, and the twelve stars such as starlight rubies. The starlight effect of corundum gemstones (red, sapphire) is best.
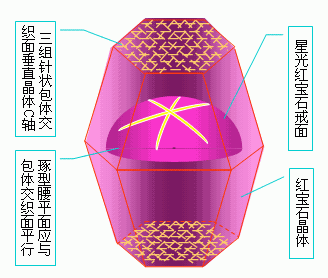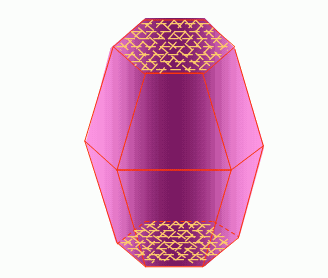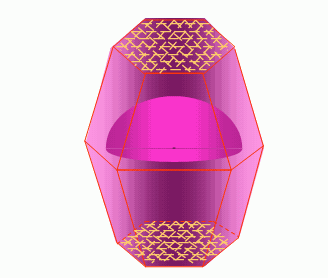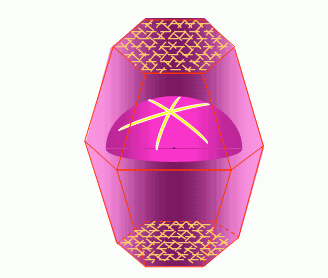

(3) Moonlight effect. Moonstone is a kind of micro-plagioclase gemstone. After polishing, it shows a kind of awkward "moon color" (azure milky white halo). This is caused by the internal fine lattice-like twin crystal structure.


(4) Color change effect. Some gems can behave differently in different shades of light. Typically, gold emeralds appear green in daylight and purplish red in incandescent or waxy light. In addition, green sapphire in Thailand and vanadium-containing sapphire in Colombia also have a discoloration effect.

(5) Color change effect. Mainly due to the diffraction effect of light, red, blue, green, yellow and other color conversion phenomena appear on the surface of the gemstone, which is called color change. This phenomenon is a typical feature of opal stone (precious opal), which is tangible in the form of flakes and bands, which is different from "fire" (just flashing color).

Embroidery Shirts,Long-Sleeve Clothing Shirts,Polyester Suede Men'S Shirt,Embroidery Men'S Shirts
SHAOXING UNIVERSE IMPORT AND EXPORT CO.,LTD , https://www.zjshirts.com